Key Takeaways
Trial Updates:
- Adjuvant nivolumab (CheckMate 274): Reduced recurrence in high-risk MIBC.
- Neoadjuvant disitamab vedotin + toripalimab (RC48-C017): High pathological complete response in HER2+ MIBC.
- FGFR3 inhibitor LY3866288 (FORAGER-1): 41% response rate in FGFR3-altered urothelial carcinoma.
- ADSTILADRIN: Encouraging gene therapy data in BCG-unresponsive NMIBC.
Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs):
- Enfortumab vedotin (EV-301): 41.3% ORR, 5.55-month PFS, 12.9-month OS (FDA-approved).
- Sacituzumab govitecan (TROPiCS-04): 23% ORR, 4.2-month PFS, 10.3-month OS (FDA approval withdrawn).
- HER2-ADCs: Trastuzumab deruxtecan & disitamab vedotin show promising early-phase data.
Future Outlook:
- ADC + Immunotherapy combos may enhance responses and overcome resistance.
- ADCs are redefining bladder cancer treatment strategies.
26 February 2025
ASCO GU 2025 Symposium was a pivotal event in the landscape of bladder cancer research and treatment. With rapid advancements in immunotherapy, antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), targeted therapies, and novel biomarkers, this year’s meeting reshaped clinical practice and offered new hope for patients. Major trials data that were presented at the conference includes:
| Adjuvant Nivolumab in High-Risk Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer (CheckMate 274 Trial) | Dr. Matthew I. Milowsky presented updated efficacy outcomes, including overall survival data, for patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer receiving adjuvant nivolumab versus placebo. The findings underscore the potential of nivolumab in reducing recurrence risk in high-risk patients. |
| Neoadjuvant Disitamab Vedotin Plus Toripalimab in HER2-Positive MIBC | Dr. Xinan Sheng reported on the RC48-C017 trial, evaluating the combination of disitamab vedotin and toripalimab as neoadjuvant therapy in HER2-expressing muscle-invasive bladder cancer. Updated efficacy and safety results demonstrated promising pathological complete response rates, suggesting a potential new therapeutic avenue for this subset of patients. |
| First-in-Human Study of LY3866288 (LOXO-435) in FGFR3-Altered Advanced Solid Tumors | Dr. Gopa Iyer presented initial results from the FORAGER-1 study, assessing LY3866288, a potent and selective FGFR3 inhibitor, in patients with FGFR3-altered metastatic urothelial carcinoma. The study reported a 41% confirmed response rate and a 90% disease control rate, highlighting LY3866288’s potential as a targeted therapy. |
| Real-World Outcomes of ADSTILADRIN (Nadofaragene Firadenovec-VNCG): | New data on ADSTILADRIN, a novel gene therapy for non-muscle invasive bladder cancer unresponsive to BCG, were presented, offering insights into its efficacy and safety in a real-world setting. These findings may influence future therapeutic approaches for this challenging patient population. |
Antibody Drug Conjugates in Bladder Cancer:
The key antibody drug conjugates in metastatic urothelial cancer include enfortumab vedotin, sacituzumab govitecan, trastuzumab deruxtecan, and disitamab vedotin.
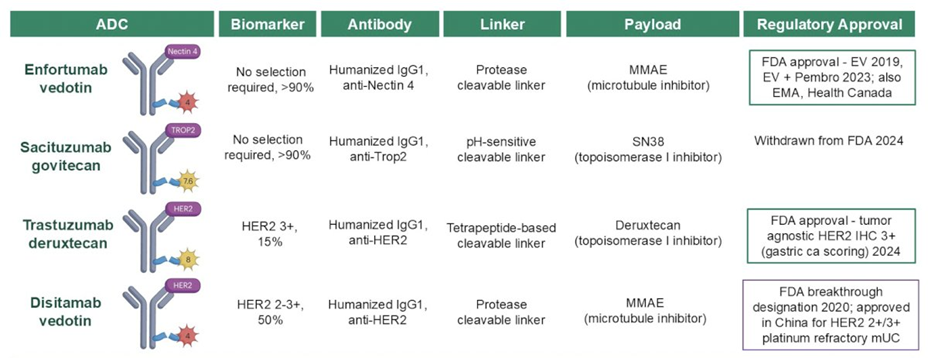
Source: UroToday1
Antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) monotherapy has emerged as a crucial option for patients with advanced bladder cancer following platinum-based chemotherapy and immune checkpoint inhibitors. Among the FDA-approved ADCs in this setting, enfortumab vedotin demonstrated significant efficacy in the phase III EV-301 trial. This study included 608 patients who were randomized to receive enfortumab vedotin or taxane/vinflunine. The results showed an objective response rate (ORR) of 41.3%, a median progression-free survival (PFS) of 5.55 months, and a median overall survival (OS) of 12.9 months.
Another ADC under investigation in this space is sacituzumab govitecan, evaluated in the TROPiCS-04 Cohort 3 trial. Patients were randomized to receive either sacituzumab govitecan or taxane/vinflunine, with outcomes revealing an ORR of 23%, a median PFS of 4.2 months, and a median OS of 10.3 months. However, FDA approval for sacituzumab govitecan in this indication was later withdrawn.
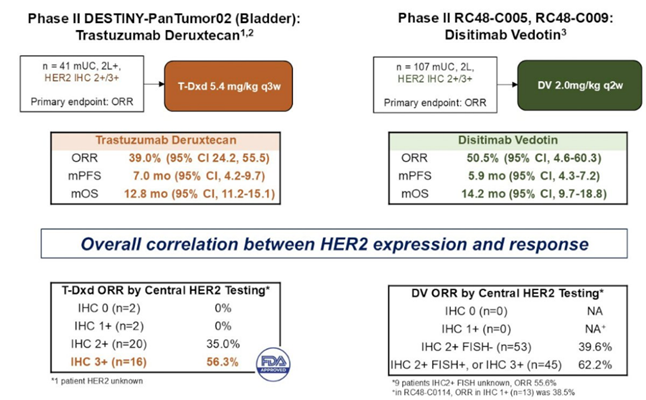
Additionally, HER2-targeted ADCs have shown promising activity in early-phase clinical trials. Dr. Di Maria Jiang highlighted the development of ADCs targeting HER2, a protein overexpressed in a subset of bladder cancers. Agents like trastuzumab deruxtecan and disitamab vedotin have demonstrated encouraging activity in early-phase studies, offering potential new avenues for patients with HER2-positive tumors. The phase II DESTINY-Pan Tumor02 (Bladder) trial is assessing the efficacy of trastuzumab deruxtecan, while disitamab vedotin is being evaluated in the phase II RC48-C005 and RC48-C009 studies. These therapies are currently under investigation to confirm their efficacy and safety profiles.
These developments highlight the growing potential of ADCs in bladder cancer treatment, particularly in patients who have progressed on prior therapies.
Dr. Terence Friedlander discussed the potential of combining ADCs with other treatments to overcome resistance and improve outcomes in metastatic urothelial carcinoma. He emphasized the importance of selecting combinations that minimize overlapping toxicities and enhance target antigen expression. Notably, combining ADCs with immunotherapies has shown promise, as ADCs can induce immunogenic cell death, potentially enhancing the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibitors. Ongoing trials are exploring these combinations to determine their clinical benefits.
These discussions at ASCO GU 2025 underscore the dynamic and evolving role of ADCs in bladder cancer therapy, highlighting the potential of combination strategies and targeted approaches to improve patient outcomes.
To get further information about the phase 3 drugs discussed as ASCO GU, and other highlights, contact us.
References:
- UroToday 2025, ASCO GU 2025: Targeting Bladder Cancer with Antibody Drug Conjugates
- Lock et al. 2025, Safety of combining radiotherapy and antibody drug conjugates in advanced urothelial and other cancers, JCO 2025
- Casas et al. 2025, Efficacy and toxicity profile of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC) based combination therapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma (aUC): A systematic review of clinical trials, JCO 2025
- Mary Caffrey. 2025, Pursuit of ADCs in Bladder Cancer Comes with Questions About Toxicity, Cost, AJMC 2025

